Technical Guidelines for Installing Generators
Discover the essential technical requirements and guidelines for a successful generator installation.

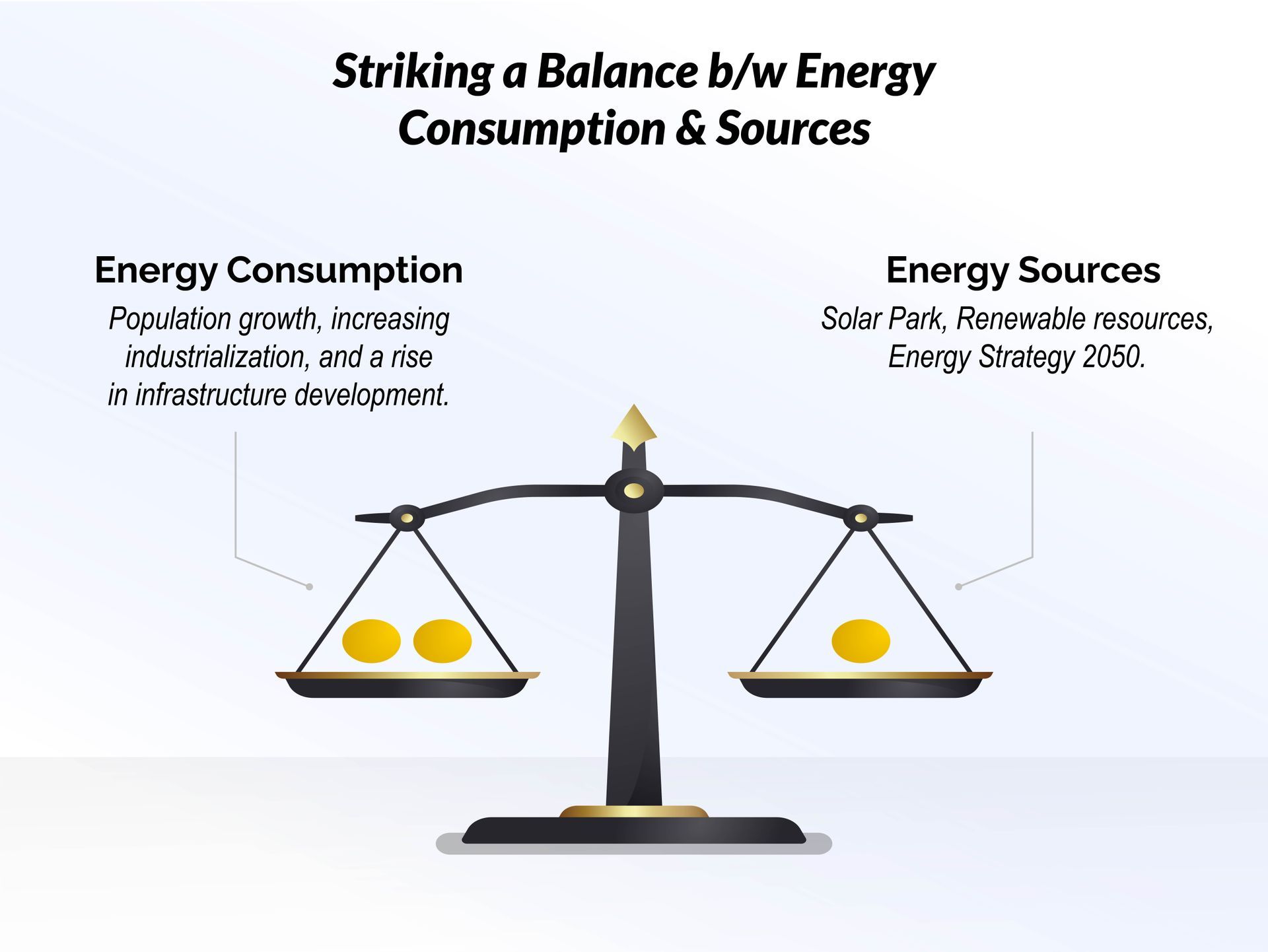
Site Assessment and Planning
Before installing a generator, it is crucial to conduct a thorough site assessment and develop a comprehensive plan. This involves evaluating the location and determining the feasibility of installing a generator. Factors to consider include the available space, accessibility, and proximity to the main electrical panel.
Additionally, it is important to assess the electrical load requirements of the site to determine the appropriate generator size. This can be done by consulting with a qualified electrician or generator professional.
A well-planned site assessment ensures that the generator installation is conducted efficiently and meets all requirements.
SITE PLANNING FOR ENCLOSED PERMANENT GENERATORS
Enclosed permanent generators require careful site planning to ensure proper installation and functionality. Here are some key considerations:
- Foundation: A solid concrete foundation is essential to support the weight of the generator. It should be level and adequately sized to accommodate the generator dimensions.
- Ventilation: Proper ventilation is crucial to prevent overheating of the generator. Sufficient airflow should be ensured by providing vents or louvers in the generator enclosure.
- Noise Control: Enclosed permanent generators can generate significant noise levels. To minimize noise disturbance, soundproofing measures such as acoustic insulation and noise barriers should be implemented.
- Accessibility: Sufficient space should be allocated for easy access to the generator for maintenance and repairs. It is important to consider the clearance requirements specified by the manufacturer.
By carefully planning the site for enclosed permanent generators, you can ensure optimal performance and longevity.
SITE PLANNING FOR ENCLOSED PORTABLE/MOBILE GENERATORS
Enclosed portable/mobile generators require specific considerations to ensure safe and efficient operation. Here are some important guidelines:
- Location: Choose a well-ventilated area for generator placement to prevent carbon monoxide buildup. Keep the generator at least 10 feet away from any structure.
- Grounding: Proper grounding is essential to protect against electrical faults. Follow the manufacturer's guidelines for grounding the generator.
- Fuel Storage: If storing fuel on-site, ensure compliance with local regulations and safety standards. Use approved containers and maintain proper ventilation for fuel storage areas.
- Mobility: Consider the weight and size of the generator when planning for transportation. Ensure the availability of suitable ramps or lifting equipment if necessary.
By following these guidelines, you can safely and efficiently plan the site for enclosed portable/mobile generators.
SITE PLANNING FOR PERMANENT GENERATORS INSTALLED INSIDE A BUILDING
Installing a permanent generator inside a building requires careful planning to ensure compliance with safety regulations. Here are some important considerations:
- Location: Choose a well-ventilated area inside the building, preferably near an exterior wall. Ensure proper clearance for generator maintenance and ventilation requirements.
- Fuel Source: Determine the appropriate fuel source for the generator based on the building's infrastructure and availability. Consider factors such as natural gas, propane, or diesel fuel.
- Exhaust System: Install an exhaust system to safely vent the generator emissions outside the building. Follow local building codes and regulations for exhaust system installation.
- Fire Safety: Implement fire safety measures, such as installing fire-rated walls and ensuring proper ventilation to prevent the buildup of combustible gases.
By addressing these considerations, you can safely install a permanent generator inside a building while complying with the necessary regulations.
Electrical Requirements
Proper electrical requirements are essential for the successful installation and operation of a generator. Here are some key points to consider:
- Load Calculation: Determine the electrical load requirements of the site to select the appropriate generator size. Consider both the starting and running wattage of the connected electrical devices.
- Transfer Switch: Install a transfer switch to safely transfer the electrical load from the main power source to the generator during a power outage. This prevents backfeeding and protects utility workers.
- Wiring: Ensure proper wiring and electrical connections between the generator, transfer switch, and main electrical panel. It is recommended to hire a licensed electrician for this task.
- Grounding: Follow the National Electrical Code (NEC) guidelines for grounding the generator and associated electrical components.
By meeting the electrical requirements, you can ensure the safe and efficient operation of the generator.
Fuel Source Considerations
Choosing the right fuel source is crucial for generator installation. Consider the following points when selecting a fuel source:
- Availability: Assess the availability of different fuel sources in your area. Consider factors such as accessibility, delivery options, and potential disruptions in fuel supply.
- Storage: Determine the appropriate storage capacity for the selected fuel source. Follow safety regulations for fuel storage to prevent leaks, spills, and fire hazards.
- Long-Term Costs: Compare the long-term costs of different fuel sources, including the initial installation costs, fuel prices, and maintenance requirements.
- Environmental Impact: Consider the environmental impact of the chosen fuel source. Evaluate factors such as emissions, carbon footprint, and sustainability.
By carefully considering these fuel source considerations, you can make an informed decision for your generator installation.
Safety Precautions
Ensuring safety during generator installation is of utmost importance. Here are some essential safety precautions:
- Carbon Monoxide (CO) Detection: Install CO detectors in the vicinity of the generator and inside the building to prevent CO poisoning. Regularly test and maintain the detectors.
- Ventilation: Provide adequate ventilation for enclosed generator installations to prevent the buildup of harmful gases. Follow the manufacturer's guidelines for proper ventilation requirements.
- Fire Safety: Implement fire safety measures, such as installing fire extinguishers and ensuring proper clearance from flammable materials.
- Electrical Safety: Adhere to electrical safety protocols, such as proper grounding, using appropriate wiring materials, and following installation guidelines provided by the manufacturer.
By prioritizing safety precautions, you can prevent accidents and ensure the well-being of individuals during generator installation and operation.
Maintenance and Testing
Regular maintenance and testing are essential for the optimal performance and longevity of a generator. Here are some important practices to follow:
- Scheduled Maintenance: Create a maintenance schedule based on the manufacturer's recommendations. This may include oil and filter changes, spark plug replacements, and overall system inspections.
- Load Testing: Periodically conduct load testing to ensure the generator can handle the connected electrical load. This helps identify any issues or potential failures.
- Fuel Management: Regularly monitor and maintain the fuel supply to prevent fuel degradation and ensure reliable generator operation.
- Battery Maintenance: Check and replace the generator's battery as needed to ensure proper starting and operation.
By implementing a comprehensive maintenance and testing routine, you can maximize the lifespan and reliability of your generator.
Conclusion
Preparing your site for generator installation involves a comprehensive understanding of power requirements, technical data considerations, and adherence to regulatory and environmental guidelines. By incorporating statistical insights, technical specifications, and industry recommendations, you can approach the installation process in a professional and well-informed manner. Reference reputable sources and consult with qualified professionals to ensure a seamless and efficient integration of a backup power system into your site's infrastructure.
Click to Share