The Difference Between Prime & Standby - Generator Power Ratings Explained
This is a subtitle for your new post

Generators are crucial for providing electrical power during outages or in locations without access to the main power grid. When choosing a generator, understanding the difference between prime and standby power ratings is essential to ensure the generator meets your specific needs. This blog delves into the technical details, statistics, and practical applications of these two power ratings.
Understanding Generator Power Ratings
Power ratings are metrics that indicate the operational capacity of a generator. The two primary ratings are
prime power and
standby power:
Prime Power:
This rating applies to generators that operate as the primary source of power. These generators run for an unlimited number of hours per year in variable load applications. They are ideal for remote sites, such as mining operations or remote construction projects, where no utility power is available.
Standby Power:
This rating is used for generators that provide emergency power during unexpected outages. They are designed to operate for the duration of the power outage but not for prolonged use. Typically, standby generators are rated to run for up to 200 hours per year.
Technical Differences
Operating Hours and Load Capacity
- Prime Generators: Capable of running continuously with an average load factor of 70-80%. They can handle varying loads, including spikes, making them suitable for industrial and commercial applications where power needs fluctuate.
- Standby Generators: Designed for short-term use with a 100% load factor but only during emergencies. They are not built to run continuously or handle large fluctuations in power demand.
Maintenance and Durability
- Prime Generators: Require regular maintenance due to their continuous operation. They are built with more robust components to withstand the rigors of constant use.
- Standby Generators: Maintenance is typically less intensive because of limited use. However, they need regular checks to ensure they are ready for an emergency.
Cost and Fuel Efficiency
- Prime Generators: Generally more expensive due to their heavy-duty construction and advanced cooling systems. They also consume more fuel over time due to continuous operation.
Standby Generators: Lower upfront costs but potentially higher operational costs per hour if used beyond their intended emergency use.
Applications and Use Cases
Prime Power Applications
- Remote Industrial Sites: Mining, oil, and gas operations often require prime power generators due to the absence of a stable power grid.
- Construction: Sites without power infrastructure rely on prime generators for tools, lighting, and temporary facilities.
- Agriculture: Farms in remote areas may use prime generators for irrigation systems, storage facilities, and processing equipment.
Standby Power Applications
- Hospitals: Standby generators ensure critical medical equipment remains operational during outages.
- Data Centers: To prevent data loss and ensure uptime, data centers use standby generators as a backup power source.
- Residential: Homeowners use standby generators to maintain power during storms or grid failures.
Statistics and Data
Market Insights
- The global generator sales market was valued at approximately USD 20 billion in 2022 and is expected to reach USD 27 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 6.2%.
- Prime generators account for about 40% of the market share, primarily driven by the industrial sector's demand.
- Standby generators dominate the residential and commercial sectors, holding around 60% of the market.
Performance Metrics
- Fuel Efficiency: Prime generators typically consume 0.25 to 0.35 liters of fuel per kWh produced, while standby generators may consume 0.28 to 0.40 liters per kWh during short-term use.
- Operational Lifespan: Prime generators have an expected operational lifespan of 15,000 to 20,000 hours, whereas standby generators are usually rated for around 2,500 to 3,000 hours.
| Feature | Prime Generator | Standby Generator |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Hours | Continous | upto 200 hours per year |
| Load Capacity | 70 - 80% average load | 100% load for short durations |
| Maintenance | High | Moderate |
| Initial Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Fuel Efficiency | Moderate | Variable |
| Lifespan (hours) | 15,000 to 20,000 hours | 2,500 to 3,000 |
Table 1: Comparison of Prime and Standby Generators
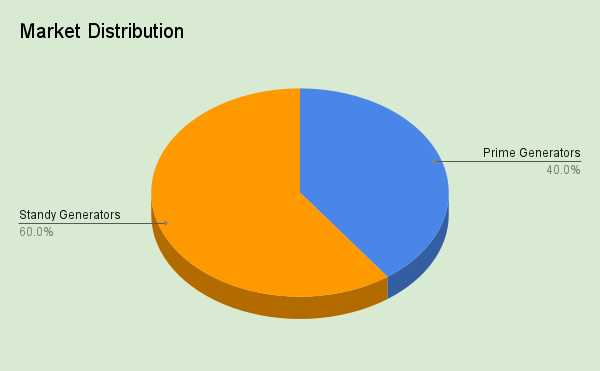
Figure 1: A pie chart showing the market distribution with 40% for Prime Generators and 60% for Standby Generators.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between prime and standby power ratings is crucial for selecting the right generator. Prime generators offer robust, continuous power for demanding environments, while standby generators provide essential backup during emergencies. Assessing your power needs and application scenarios will help you make an informed decision, ensuring reliability and efficiency.
Click to Share